Brazilian physicist has developed underwater turbines that can be much more efficient than traditional wind turbines. Just a single turbine can generate clean energy for 22 homes.
In the midst of companies' search for renewable forms of generating energy, since 80% of the world's energy generates polluting gases, the Brazilian physicist may have found a way to do this. The company has developed a new generation of underwater turbines which are much smaller, generate more energy than wind turbines and were developed specifically to capture energy in the ocean.
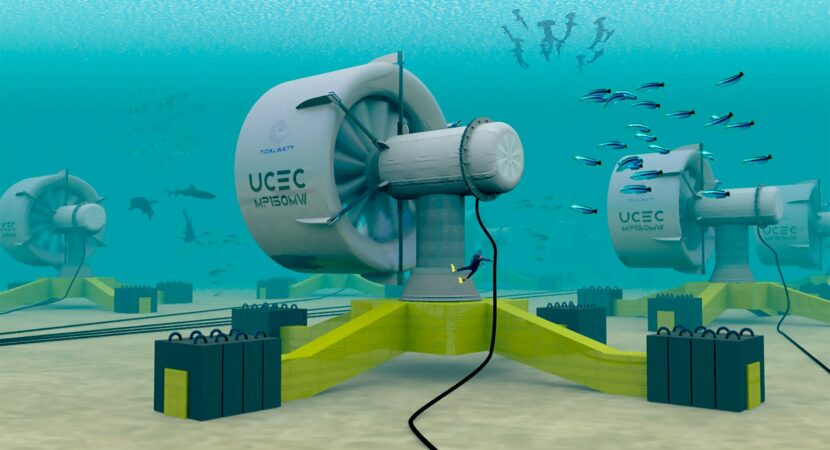
Underwater turbines measure 3m and can generate 5 MW of power
According to Maurício Queiroz, founder and CEO of the startup, when the energy source is predictable and constant, as is the exclusive case of the ocean, it is possible to say that this source guarantees energy security.
In this way, the ocean is the only source of safe clean energy. Ocean currents are already extensively mapped around the world, so we already know several positions for the installation of these underwater turbines.
The product is uniquely designed to capture hydrokinetic energy associated with underwater currents. Unlike wind turbines, this technology is not based on wind or aeronautical mechanisms, which lose energy between the wind turbine blades, but rather continuously captures the energy generated by the upstream currents.
Queiroz explains that an underwater turbine 3 m in diameter has the capacity to generate 5 MW of power at a current of 1,87 knots, practically the same power as a wind turbine 180 m in diameter. In this way, the turbine with a diameter 60 times smaller, generates the same power. In addition, due to the availability of the source, a wind turbine generates energy 90% of the time, that is, being 3,6 times smaller in coverage area, since the startup's turbines can generate 3 times more energy.
Just one underwater turbine can generate energy for 22,8 families
Startup plans to install its turbines in locations with average current speeds above 1 knot, generating 5 MW with turbine capacity varying between 70 and 95%. Considering the average energy consumption of Brazilian homes, Queiroz says that each of these turbines can serve around 22.800 families.
The executive points out that when we talk about energy generation capacity, we are talking about how much energy available in nature can be transformed into electricity. Regarding the ocean, it depends on the infrastructure that will be built with the investments to meet the demand of different locations.
The company also focuses on protecting marine life, as the installation sites have been chosen away from coral reefs so that the surrounding ecosystems are protected, avoiding trawling on the ocean floor. As well as the bases of some wind turbine plants, artificial reefs will be formed to allow various marine species to live and reproduce safely there.
environmental benefits
The Brazilian physicist's technology promises environmental and economic benefits and aligns with SDGs 7,13, 14 and XNUMX, on clean and affordable energy, action against climate change and life under water, respectively.
The system was developed to transform economically inactive and uninhabited ocean areas into sources of income without disturbing the surrounding ecosystems and without generating any visual or noise pollution. The structures are much smaller than wind turbines, therefore easier to maintain, and more versatile, and can be installed in rivers without the negative effects of hydroelectric plants.